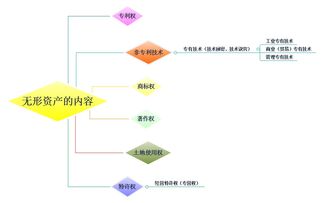
法律摩托车可以上高速吗
Understanding Legal Motions: Types, Procedures, and Best Practices
In legal proceedings, motions play a pivotal role in shaping the course of a case. They are formal requests made to a judge for a ruling or order to advance the litigation process. Understanding the types, procedures, and best practices associated with motions is crucial for both legal professionals and individuals navigating the legal system. Let's delve into the intricacies of legal motions.
What is a Motion?
A motion is a written or oral request made by one party to a case, asking the court to issue a ruling or order on a specific matter. Motions can address a wide range of issues, from procedural matters to substantive legal issues. They serve as a tool for parties to assert their rights, seek relief, or challenge the actions of the opposing party.
Types of Motions:
1.
Procedural Motions:
These motions pertain to the procedural aspects of the case, such as requests for extensions of time, requests to amend pleadings, or motions to compel discovery.2.
Substantive Motions:
Substantive motions involve the merits of the case itself. Examples include motions for summary judgment, motions to dismiss, and motions for injunctive relief.3.
PreTrial Motions:
These motions are filed before the trial begins and may address issues such as jurisdiction, venue, or the admissibility of evidence.4.
PostTrial Motions:
Filed after the trial concludes, posttrial motions include motions for a new trial, motions to set aside a verdict, or motions for judgment notwithstanding the verdict (JNOV).5.
Interlocutory Motions:
These are motions filed during the course of litigation, addressing specific issues that arise before the final resolution of the case.Procedures for Filing a Motion:

1.
Drafting the Motion:
The party seeking relief must draft a written motion that clearly articulates the legal and factual basis for the request. The motion should cite relevant statutes, case law, and supporting evidence.2.
Filing with the Court:
The motion, along with any supporting documents, is filed with the court and served on the opposing party in accordance with procedural rules and deadlines.3.
Response:
The opposing party has an opportunity to respond to the motion, either in writing or orally during a hearing. They may present counterarguments and evidence to oppose the relief sought.4.
Hearing:
Depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the motion, the court may schedule a hearing to allow both parties to present their arguments orally. In some cases, the court may issue a ruling based solely on the written submissions.5.
Decision:
After considering the arguments presented by both parties, the court will issue a ruling either granting or denying the motion. The court may also issue specific orders or directives based on its decision.Best Practices for Filing and Responding to Motions:
1.
Thorough Preparation:
Whether drafting a motion or responding to one, thorough preparation is essential. Conduct comprehensive legal research, gather relevant evidence, and craft persuasive arguments supported by case law and statutes.2.
Clarity and Conciseness:
Ensure that motions are clearly written and free of unnecessary legal jargon. Judges appreciate concise and wellorganized arguments that get straight to the point.3.
Timeliness:
Adhere to procedural deadlines for filing motions and responding to them. Failure to comply with deadlines can result in the waiver of rights or sanctions imposed by the court.4.
Professionalism:
Maintain a professional demeanor in all interactions related to motions, both in written submissions and oral arguments. Respect for the court and opposing counsel is paramount.5.
Strategic Considerations:
Consider the strategic implications of filing or responding to a motion. Consult with experienced legal counsel to assess the potential risks and benefits before taking action.Conclusion:
Legal motions play a vital role in the litigation process, allowing parties to assert their rights, seek relief, and shape the outcome of a case. By understanding the types, procedures, and best practices associated with motions, legal professionals and litigants can navigate the complexities of the legal system more effectively. Whether drafting a motion or responding to one, careful preparation, adherence to procedural rules, and strategic thinking are essential for achieving favorable outcomes in legal proceedings.